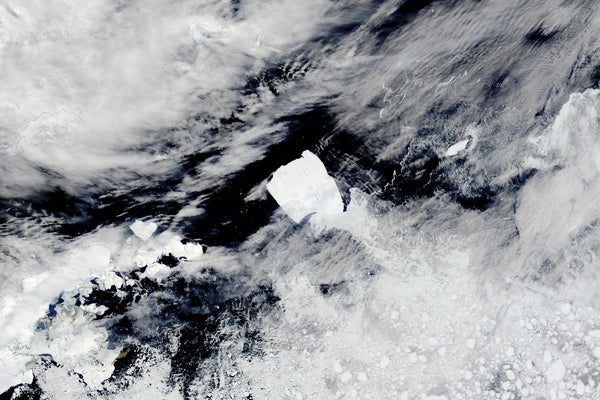
The world's largest iceberg, A23a, is on the move after being trapped in place off Antarctica's coastline for almost 40 years. The gigantic "ice island," which is three times the size of New York City, will likely drift into the "iceberg graveyard," potentially putting it on a collision course with an important penguin refuge before it fractures and melts away.
The berg, which has a surface area of around 1,550 square miles (4,000 square kilometers), was originally birthed in 1986 when it calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf. But the hefty berg got stuck soon after when its submerged keel became lodged on the seafloor in the Weddell Sea.
A23a has held the title of the world's largest iceberg on multiple occasions as other, more massive ice slabs came and went while it sat in place, Christopher Shuman, a glaciologist at the University of Maryland and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, told Live Science in an email.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The elderly ice mass most recently regained its title in June, when the previous record-holder A76a ripped apart after being flung toward the equator by ocean currents.
On Nov. 25, major news outlets reported that A23a had finally started to move. However, the berg's bid for freedom actually began in 2020 when it started to become unstuck from its seafloor tether, the BBC reported.
Satellite imagery shared on X (formerly known as Twitter) by the British Antarctic Survey shows that A23a finally began moving from its sticking point in January this year. It has since traveled hundreds of miles along Antarctica's coastline.
A23a became stuck due to the thickness of its ice. Icebergs of this size can be up to 1,300 feet (400 meters) tall from top to bottom, with around 90% of its mass submerged, Shuman said.
Being stuck in place for decades is "not uncommon" for icebergs of this size, Shuman said. Early Antarctic explorers referred to them as "ice islands," he added.
These trapped bergs are able to maintain most of their ice mass because they are so large and stay close to Antarctica. It is unclear how much water is trapped inside the berg, but A68 — another former world's largest iceberg, which was around the same size as A23a is now — dumped more than 1 trillion tons of water into the ocean during its lifetime.
A23a likely became unstuck as ice on its underside melted from below, which reduced its weight and lifted it off the seafloor. This eventually happens to all stranded icebergs and was likely not related to climate change, the BBC reported.
A23a will be pushed north by ocean currents into the Drake Passage, also known as the iceberg graveyard — a body of water that most other large icebergs born into the Weddell Sea, including A76a and A68a, have passed through on their slow marches to their watery graves.
This area contains several islands that the bergs can occasionally bump into, including South Georgia — an inhabited island in the Southern Ocean that is home to massive penguin colonies. In 2020, A68a was on a collision course with South Georgia, which greatly concerned scientists due to its potential for disrupting the penguins' feeding capabilities. However, the berg narrowly avoided the island before fracturing into more than a dozen of smaller pieces.
South Georgia could be in A23a's path, raising fears of another possible collision in the future. But this "isn't a certainty," Shuman said.
If A23a misses South Georgia, its size could mean it survives as far north as South Africa, where it could majorly impact shipping routes, researchers told Reuters. However, Shuman believes that fracture lines in the berg could make it more susceptible to breaking apart before it gets this far.
Scientists will continue to track the iceberg's movements to narrow down where it may go next.
Copyright 2023 LiveScience, a Future company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.