
Astronomers Just Saw a Star Eat a Planet for the First Time
A dying star swallowing a giant planet hints at the fate awaiting our solar system some five billion years from now
Charles Q. Choi is a frequent contributor to Scientific American. His work has also appeared in The New York Times, Science, Nature, Wired, and LiveScience, among others. In his spare time, he has traveled to all seven continents.

Astronomers Just Saw a Star Eat a Planet for the First Time
A dying star swallowing a giant planet hints at the fate awaiting our solar system some five billion years from now
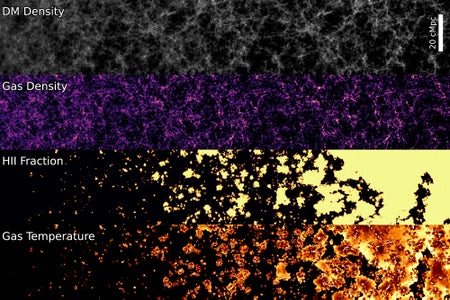
New Record-Breaking Simulation Sheds Light on ‘Cosmic Dawn’
THESAN—the largest, most detailed computer model of the universe’s first billion years yet made—is helping set expectations for observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope
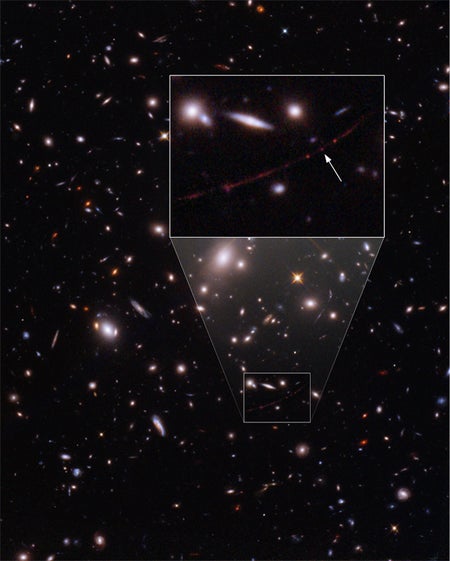

Hubble Space Telescope Spots Most Distant Star Ever Seen
Called Earendel, the star is nearly 13 billion light-years from Earth

Buried ‘Lakes’ on Mars May Just Be Frozen Clay
Mineral deposits, not salty water, are the most likely cause of radar reflections spotted beneath the planet’s south pole, a new study finds
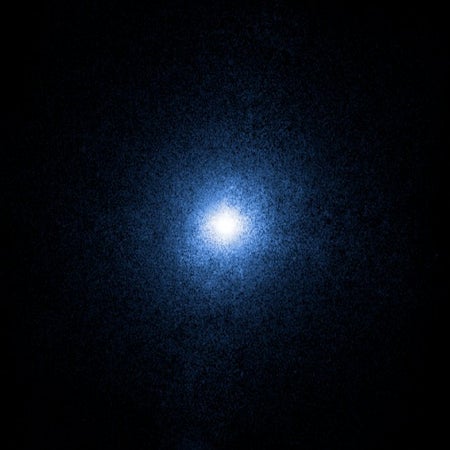

Astronomers Just Upsized an Iconic Black Hole
Cygnus X-1, the first black hole ever discovered, is significantly bigger than previously believed

Mystery of Spinning Atomic Fragments Solved at Last
New experiments have answered the decades-old question of how pieces of splitting nuclei get their spins

Jupiter and Saturn’s Great Conjunction Is the Best in 800 Years—Here’s How to See It
The giant planets will appear spectacularly close together in Earth’s sky during the solstice on December 21

3-D Printing inside the Body Could Patch Stomach Ulcers
In vivo bioprinting might also help repair hernias and treat infertility

Could Carbon-Foam Probes Sail to Nearby Stars?
Boosted by sunlight, “bubblecraft” might reach Proxima Centauri after a 185-year voyage

Surprise! Pluto May Have Possessed a Subsurface Ocean at Birth
The dwarf planet could be a more habitable world than scientists had thought
“Punch Card” DNA Could Mean Cheaper High-Capacity Data Storage
The new method may be faster and easier than other genetic storage attempts

Space Heater: Scientists Find New Way to Transfer Energy Through a Vacuum
Nanoscale experiments reveal that quantum effects can transmit heat between objects separated by empty space
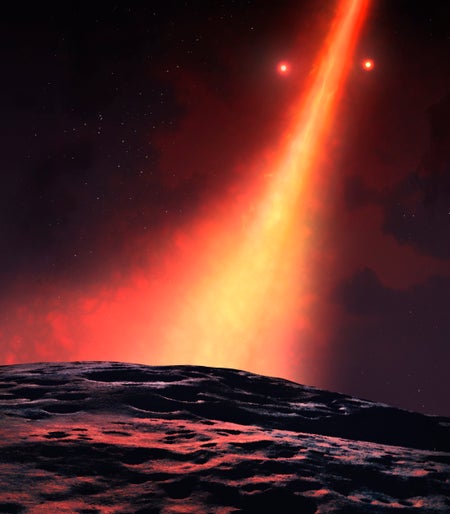

Weird Star System’s Planet-Forming Disk Goes Vertical Like a Ferris Wheel
Worlds with off-kilter orbits may be much more common than previously believed
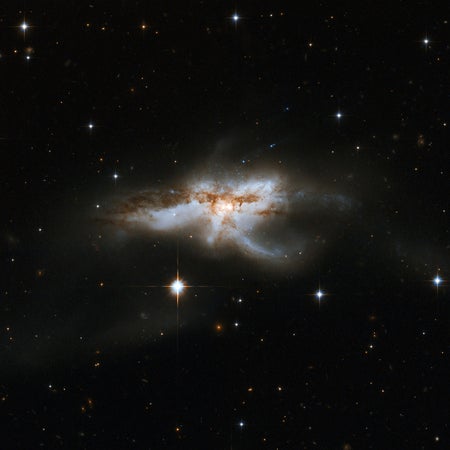

Supermassive Black Holes Collide in Galactic Merger Grand Finales
Astronomers have observed new details of black-hole growth previously hidden by obscuring clouds of gas and dust

Giant Ice Volcanoes Once Covered Dwarf Planet Ceres
A new study suggests a strange and surprisingly lively geological cycle for the small world
Is Gravity Quantum?
The ongoing search for the graviton—the proposed fundamental particle carrying gravitational force—is a crucial step in physicists’ long journey toward a theory of everything
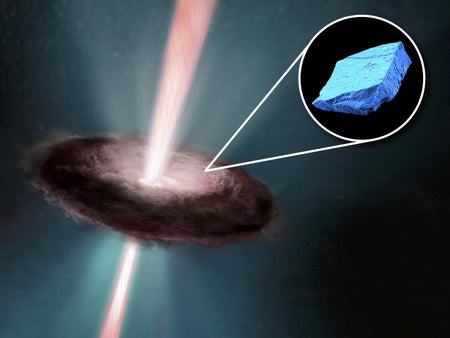
Blue Meteorite Crystals Reveal the Sun’s Wild Youth
Ancient relics confirm our solar system’s tempestuous origins

Ingredients for Life Found on Saturn's Moon Enceladus
A new look at old data from NASA’s Cassini orbiter shows complex organic molecules are gushing from the tiny moon

Surprise! Jupiter’s Lightning Looks a Lot Like Earth’s
Data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft reveals thunderbolts around the giant planet’s stormy poles

What Made Saturn’s Ravioli-Shaped Moons?
New research suggests collisions between moonlets created the oddly-formed objects

Building Sails for Interstellar Probes Will Be Tough, but Not Impossible
A new study validates the feasibility of constructing gossamer-thin light sails for propelling spacecraft to other stars
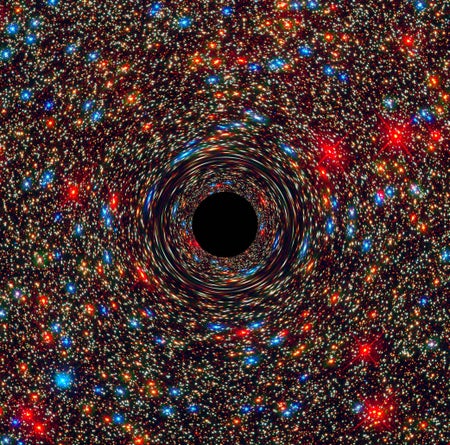

Black Hole Pretenders Could Really Be Bizarre Quantum Stars
New research reveals a possible mechanism allowing “black stars” and “gravastars” to exist

When AI Steers Us Astray
A new debugging tool can pinpoint errors that cause neural networks to make mistakes

Oldest Supermassive Black Hole Found from Universe’s Infancy
The object grew to more than 800 million times the mass of the sun when the cosmos was only 5 percent its present age